Revolutionizing Manufacturing: Top Industrial Automation Solutions and Providers in the US
Discover how industrial automation boosts productivity, quality, and flexibility in manufacturing. For more information, use a quick search below.
The industrial automation sector in the US plays a pivotal role in driving innovation and efficiency across various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and more. As the demand for operational precision and reduced downtime grows, businesses are increasingly turning to automation to stay competitive. The US market, contributing significantly to the global $200 billion industrial automation industry, is expected to grow at an impressive rate, fueled by advances in robotics, AI, and IoT.
What is Industrial Automation?
Industrial automation integrates advanced technologies like robotics, control systems, software, and IoT to replace manual labor with automated processes. From smart factories equipped with AI-driven systems to robotic arms assembling components with precision, automation has revolutionized how businesses operate.
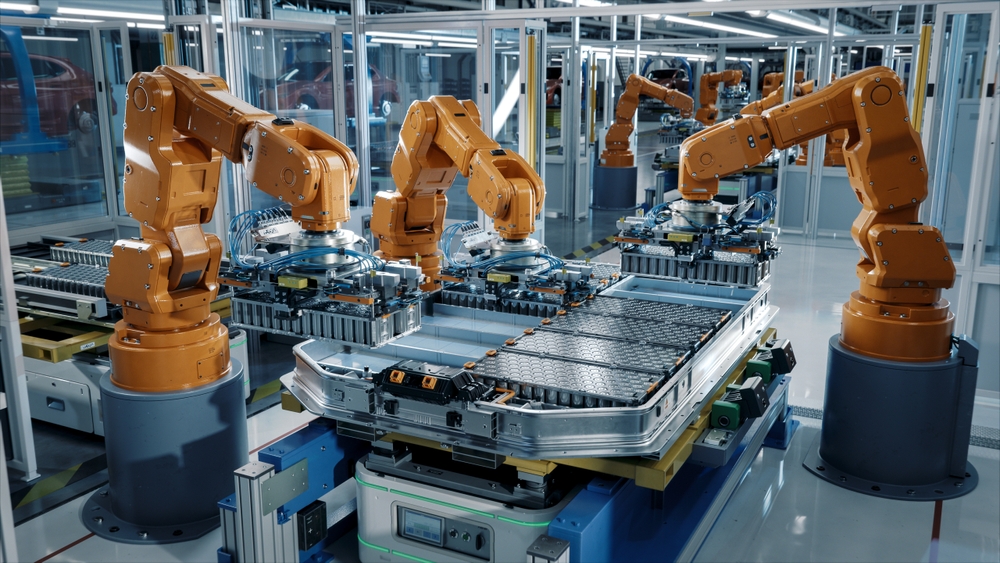
Key benefits include:
- Efficiency: Automated systems can operate 24/7, minimizing downtime and increasing output.
- Precision: Automation reduces human error, ensuring consistency and quality.
- Cost Reduction: While initial investments can be significant, automation lowers long-term operational costs.
- Safety: Automation eliminates human involvement in hazardous environments, reducing workplace accidents.
Key Players in US Industrial Automation
1. Rockwell Automation
- Flagship Products:
- Allen-Bradley Control Systems: The Allen-Bradley portfolio includes CompactLogix and ControlLogix PLCs, starting at $2,000. These programmable controllers offer scalable automation for industries ranging from consumer goods to automotive manufacturing.
- FactoryTalk Suite: FactoryTalk Analytics and FactoryTalk AssetCentre are part of a comprehensive software suite for real-time data collection and operational insights, starting at $1,500/license annually.
- Benefits:
Rockwell Automation’s solutions are renowned for their flexibility and integration capabilities. For example, in the food and beverage industry, their systems enable batch control processes that improve accuracy and compliance with FDA standards.
2. Siemens USA
- Flagship Products:
- SIMATIC PLCs: These advanced controllers, starting at $1,500, are designed for high-speed, precision manufacturing applications.
- MindSphere: This IoT platform collects and analyzes data from industrial devices, enhancing predictive maintenance and overall operational efficiency. Pricing starts at $100/month per connected device.
- Tia Portal: A fully integrated automation software suite that allows seamless engineering of PLCs, HMIs, and other devices, priced at $2,000 per license.
- Benefits:
Siemens is a leader in digitalization, helping industries transition to smart factories. Its solutions enable real-time decision-making, energy savings, and streamlined production cycles. Automotive manufacturers particularly benefit from Siemens’ capabilities in robotic welding and assembly.
3. ABB Robotics and Automation
- Flagship Products:
- IRB 6700 Industrial Robots: Starting at $50,000, these robots perform tasks like painting, welding, and material handling with high precision.
- ABB Ability™ Smart Sensors: Priced at $300 per unit, these sensors enable condition monitoring and predictive maintenance for machinery.
- RobotStudio: A virtual commissioning software allowing offline programming of ABB robots, priced at $5,000/license.
- Benefits:
ABB’s robotics solutions cater to industries ranging from electronics to pharmaceuticals. For instance, its robots ensure sterile operations in pharmaceutical manufacturing, reducing contamination risks and adhering to stringent quality standards.
4. Honeywell Process Solutions
- Flagship Products:
- Experion® PKS: Starting at $20,000, this control system integrates plant-wide operations, ensuring seamless communication between devices and systems.
- Forge Software: Designed for operational efficiency and real-time performance tracking, pricing starts at $10,000/license annually.
- SmartLine Transmitters: High-accuracy sensors for monitoring pressure, flow, and temperature, priced at $1,500/unit.
- Benefits:
Honeywell specializes in process industries like oil and gas, refining, and chemicals. Its solutions enhance regulatory compliance, operational reliability, and energy efficiency. For example, oil refineries use Honeywell’s systems for precise flow control and real-time monitoring, reducing waste and maximizing output.
5. Fanuc America
- Flagship Products:
- M-20iA Robot Series: With a starting price of $25,000, these robots handle tasks like palletizing and assembly in the automotive and consumer goods industries.
- CNC Systems: Fanuc’s computer numerical control systems are priced from $3,000 and are vital for machining precision parts.
- Field System: A cloud-based analytics platform for monitoring robot performance, available for $1,500/year.
- Benefits:
Fanuc robots and systems are renowned for durability and reliability. Their automation technologies have transformed the automotive sector by enabling high-speed manufacturing and quality control, particularly in painting and welding applications.
Emerging Trends in Industrial Automation
- Adoption of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI-driven analytics enable real-time optimization of manufacturing processes, improving yield and reducing waste.
- Increased Use of Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Unlike traditional robots, cobots work alongside humans, enhancing flexibility in industries like electronics assembly.
- Expansion of IoT-Enabled Automation: IoT devices and cloud platforms like Siemens’ MindSphere are driving predictive maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime.
- Green Automation: Companies are adopting energy-efficient solutions to meet sustainability goals, such as ABB’s low-energy consumption robots.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Platforms like Honeywell Forge and FactoryTalk enable managers to oversee operations from anywhere, enhancing scalability and responsiveness.
Industrial automation in the US is shaping the future of manufacturing and beyond. Key players like Rockwell Automation, Siemens, ABB, Honeywell, and Fanuc are at the forefront, offering advanced solutions tailored to industry needs. Their products and services help businesses achieve higher efficiency, precision, and cost savings while paving the way for a smarter, more sustainable industrial landscape.
As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, investing in the right automation partner and technology will be critical for businesses to remain competitive and meet future challenges head-on.











