Exploring Optical Measurement Technology: Principles, Benefits, and Industrial Applications
Enhance your optical measurements with cutting-edge software that provides precise and reliable results. Find the perfect solution for your research or industrial needs.
In the realm of measurement technologies, the evolution from traditional tactile methods to advanced optical approaches marks a significant leap forward. Optical measurement technology, which harnesses light to evaluate the properties of objects without physical contact, presents a sophisticated alternative to the mechanical touch-based systems. This technology not only enhances the accuracy of measurements but also expands the scope of applications, from industrial manufacturing to traffic enforcement. This article delves into the principles, benefits, and varied applications of optical measurement technology, shedding light on how this innovative approach is transforming industries by providing faster, non-invasive, and versatile measurement solutions.
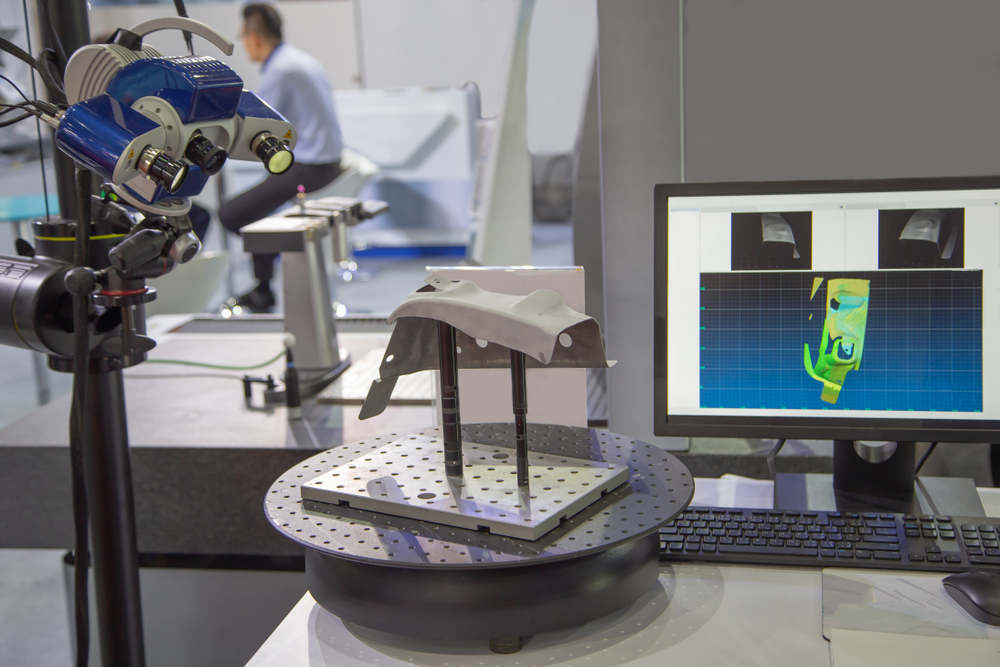
Understanding Optical Measurement Technology
Optical measurement technology employs light to conduct non-contact measurements of an object's properties, unlike tactile measurement techniques which require direct contact. This technology utilizes the principles of light absorption and reflection to assess entire surfaces rather than just isolated points. What makes optical measuring systems beneficial?
Recognized for their precision and speed, optical measurement systems provide almost instantaneous feedback due to their real-time measurement and digital transmission capabilities. These systems excel in performing complex and critical measurements and are versatile across various applications. A significant advantage of optical measurement is its non-contact nature, ensuring that the surface of the component remains undamaged and intact.
Key Universal Benefits of Optical Measuring Systems
- Non-contact and non-destructive measurements
- Rapid measurement speeds
- Applicable to all material types
- Capable of inspecting both surfaces and three-dimensional objects
Applications of Optical Measurement Methods
Optical measurement technology is versatile, finding uses in numerous fields ranging from quality assurance in manufacturing to enforcing speed limits for road safety. Blending optical with tactile measurement technologies allows for groundbreaking advancements. In the automotive sector, applications include comprehensive vehicle measurements and detailed cylinder pressure assessments.
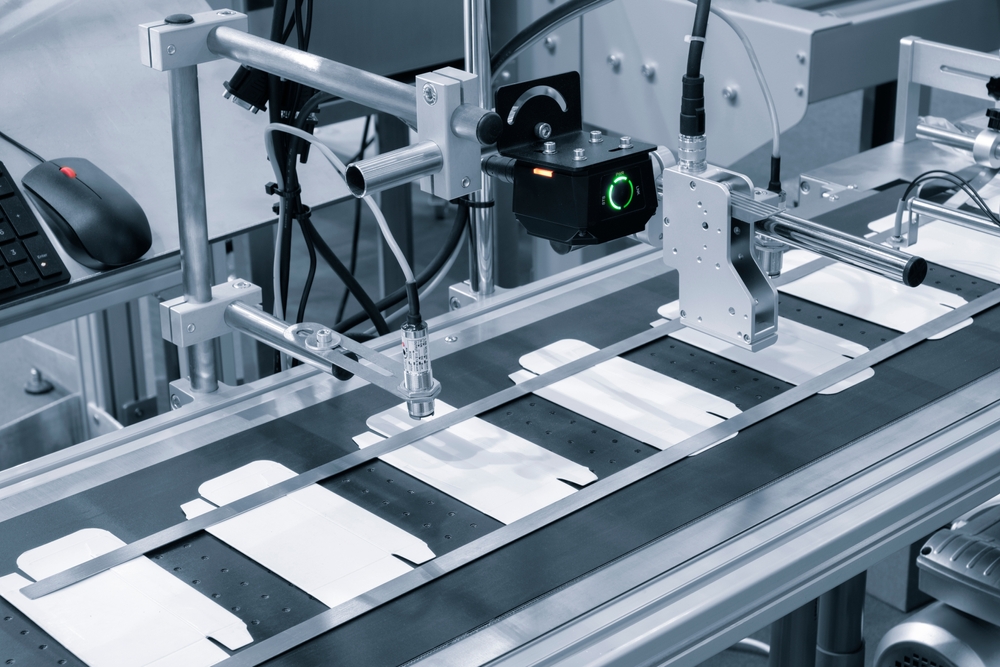
Optical Measurement Technology in Quality Assurance for Mass Production
In manufacturing, 100% monitoring with complete traceability is critical to meet rising quality standards, sometimes requiring inspections at the nanometer scale. Different high-speed optical measuring methods are employed based on the surface characteristics of the objects:
For matte (diffuse) surfaces:
- Triangulation systems using laser technology
- Structured light projection systems
- Stereoscopy
For shiny surfaces:
- Deflectometry (suitable for scanning entire vehicles)
- Interferometry
Optical Measurement Technology for Speed Monitoring
Light-barrier measuring instruments are especially effective for accurately determining vehicle speeds. These instruments use multiple light sensors in sequence to create several light barriers. When a vehicle breaks through a barrier, the instrument quickly calculates the speed based on the time taken to move between points. If the vehicle exceeds the speed limit, digital cameras within the system automatically capture the event.
Integrating Tactile and Optical Measurement Technologies in Engine Development
An innovative example is the measuring spark plug, which combines tactile and optical measurement technologies to enhance engine development. This plug integrates a high-temperature miniature pressure sensor and fiber-optic probes, linking conventional cylinder pressure measurements with visualizations of combustion chamber processes. The "optical window" function positions the probes to capture different combustion chamber areas. Optical fibers transmit light from the flame directly to an indication system, graphically displaying combustion processes. This integration allows for the analysis of phenomena such as knocking, soot formation, and pre-ignition alongside simultaneous pressure measurements, offering a more comprehensive understanding of combustion dynamics.
Optical measurement technology has firmly established itself as a cornerstone of modern measurement techniques across various industries due to its precision, speed, and non-destructive nature. From ensuring quality assurance in mass production to facilitating advanced research in engine development, optical methods provide critical data that supports innovation and efficiency. The integration of optical and tactile measurement technologies further underscores the potential for future advancements in measurement science. As industries continue to demand higher precision and greater versatility, optical measurement technologies are set to play an increasingly vital role, driving progress and enhancing capabilities in scientific and industrial fields alike.











